LightGBM algorithm
LightGBM is a high-performance gradient boosting framework that stands out for its efficiency and scalability in handling large-scale datasets. It utilizes a unique histogram-based algorithm to achieve faster training speeds and lower memory consumption compared to traditional gradient boosting methods. LightGBM employs a leaf-wise tree growth strategy, which prioritizes leaf nodes that can contribute the most to the overall loss reduction during training. This approach results in more accurate models with fewer levels in the trees. LightGBM also incorporates features like early stopping, which allows for automatic termination of training when no further improvement is observed. It supports various loss functions, provides built-in handling for categorical features, and offers advanced techniques such as bagging and feature importance analysis. LightGBM is widely adopted in machine learning tasks, particularly when dealing with large datasets and complex problems, due to its exceptional speed, memory efficiency, and strong predictive performance.
Our Implementation
At the outset, a basic LGBM model is defined using the LGBMClassifier from the LightGBM library, with a specified random state to ensure reproducibility. Subsequently, a parameter grid is set up, encompassing various values for hyperparameters such as the number of estimators (trees) in the ensemble, learning rate, number of leaves per tree, and the maximum depth of the trees.
To optimize the LGBM model's performance, the code employs the GridSearchCV technique. A GridSearchCV object is initialized with the LGBM model, the parameter grid, and the F1 score as the evaluation metric, which is particularly suited for imbalanced datasets. The use of cross-validation with 10 folds (cv=10) ensures robust parameter selection. By fitting the GridSearchCV object to the training data ('X_train_ds' and 'y_train_ds'), the process identifies the best combination of hyperparameters that yield the highest F1 score.
Following the hyperparameter tuning, a new LGBM model ('lgbm_best') is instantiated using the optimized parameter values, which is then trained on the balanced training dataset. The resulting model is expected to deliver improved fraud detection capabilities, making it well-suited for deployment in fraud prevention applications.
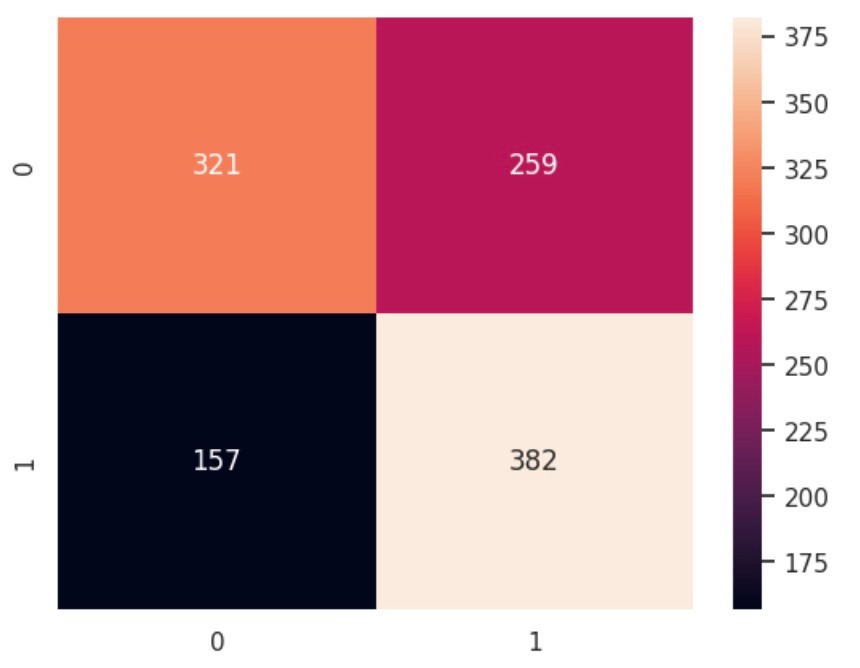
Confusion matrix: