Gradient Boosting algorithm
Gradient Boosting is a powerful machine learning technique that builds an ensemble of decision trees in a sequential manner. It focuses on minimizing the errors made by the previous trees in the ensemble by iteratively adding new trees. Each new tree is trained to correct the mistakes or residuals of the previous trees. The algorithm assigns weights to each data point based on the errors made by the previous trees, giving more weight to misclassified or poorly predicted instances. By combining the predictions of multiple trees, each one making up for the weaknesses of its predecessors, gradient boosting creates a strong predictive model. Gradient boosting is known for its ability to handle various types of data, handle both regression and classification problems, and deliver highly accurate results. Additionally, it offers flexibility through customizable loss functions and parameter tuning, allowing users to fine-tune the algorithm to their specific needs.
Our Implementation
The process begins by defining the basic GBM model using the GradientBoostingClassifier from scikit-learn, with a specified random state for reproducibility. Subsequently, a parameter grid is set up, comprising different values for the number of estimators, learning rate, and maximum depth of the trees in the ensemble.
To optimize the GBM's performance, the code utilizes GridSearchCV, a powerful tool that performs an exhaustive search over the parameter grid. The GridSearchCV object is initialized with the GBM model, the parameter grid, and the F1 score as the evaluation metric, which is well-suited for imbalanced datasets. The cross-validation with 10 folds (cv=10) ensures robust parameter selection. By fitting the GridSearchCV object to the training data ('X_train_ds' and 'y_train_ds'), the process identifies the best combination of hyperparameters that maximize the F1 score.
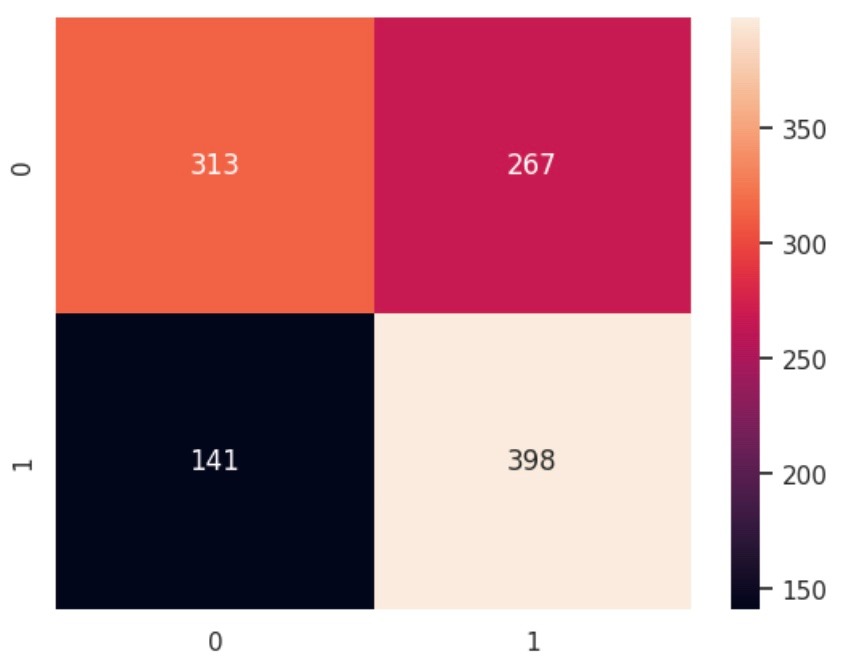
Upon obtaining the best parameters, a new GBM model ('gbm_best') is initialized using these optimized values and then trained on the balanced training dataset. The resulting model is expected to deliver enhanced fraud detection capabilities, thanks to the hyperparameter tuning process
Confusion matrix: