Random Forest algorithm
Random Forest is a versatile and powerful ensemble learning algorithm widely used for classification and regression tasks. It operates by constructing multiple decision trees during training and combining their predictions to make final predictions. Each decision tree in the random forest is trained on a random subset of the training data, with random feature selection at each split. This randomness helps to reduce overfitting and improve generalization. During prediction, the random forest aggregates the predictions of all individual trees, either by majority voting for classification or averaging for regression. This ensemble approach enhances the model's accuracy, robustness, and ability to handle high-dimensional data. Additionally, random forests provide insights into feature importance, allowing users to assess the relative importance of different features in the prediction process. Overall, random forests are highly effective and widely used due to their flexibility, ability to handle complex datasets, and excellent predictive performance.
Our Implementation
Initially, the dataset is divided into two sets: the features (X) and the corresponding labels (y), representing fraudulent transactions. Subsequently, the data is split further into training and testing sets using the 'train_test_split' function from scikit-learn.
To enhance the classifier's performance, hyperparameter tuning is employed. The GridSearchCV method is utilized to perform an exhaustive search across a predefined hyperparameter grid. This grid comprises various values for parameters like the number of estimators, maximum depth, and minimum samples split. The evaluation metric employed for this search is the F1 score, which is ideal for imbalanced datasets. The process finds the best hyperparameters, and a new Random Forest classifier is initialized ('rf_clf_best') with these optimal parameters. This tuned model is then trained on the undersampled training data ('X_train_ds' and 'y_train_ds') to create a final model with improved fraud detection capabilities.
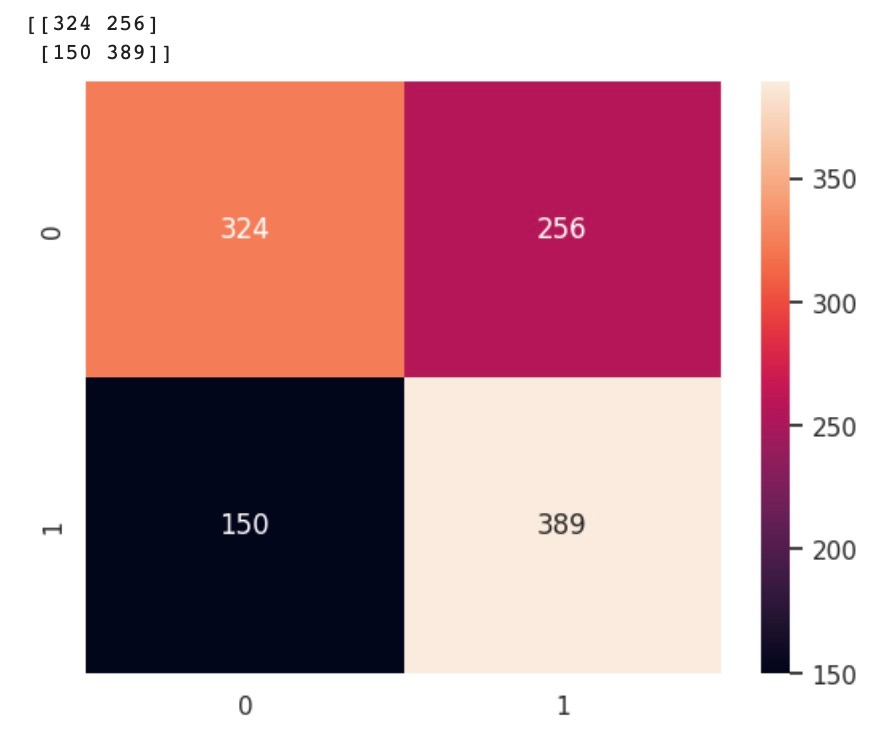
Confusion matrix: